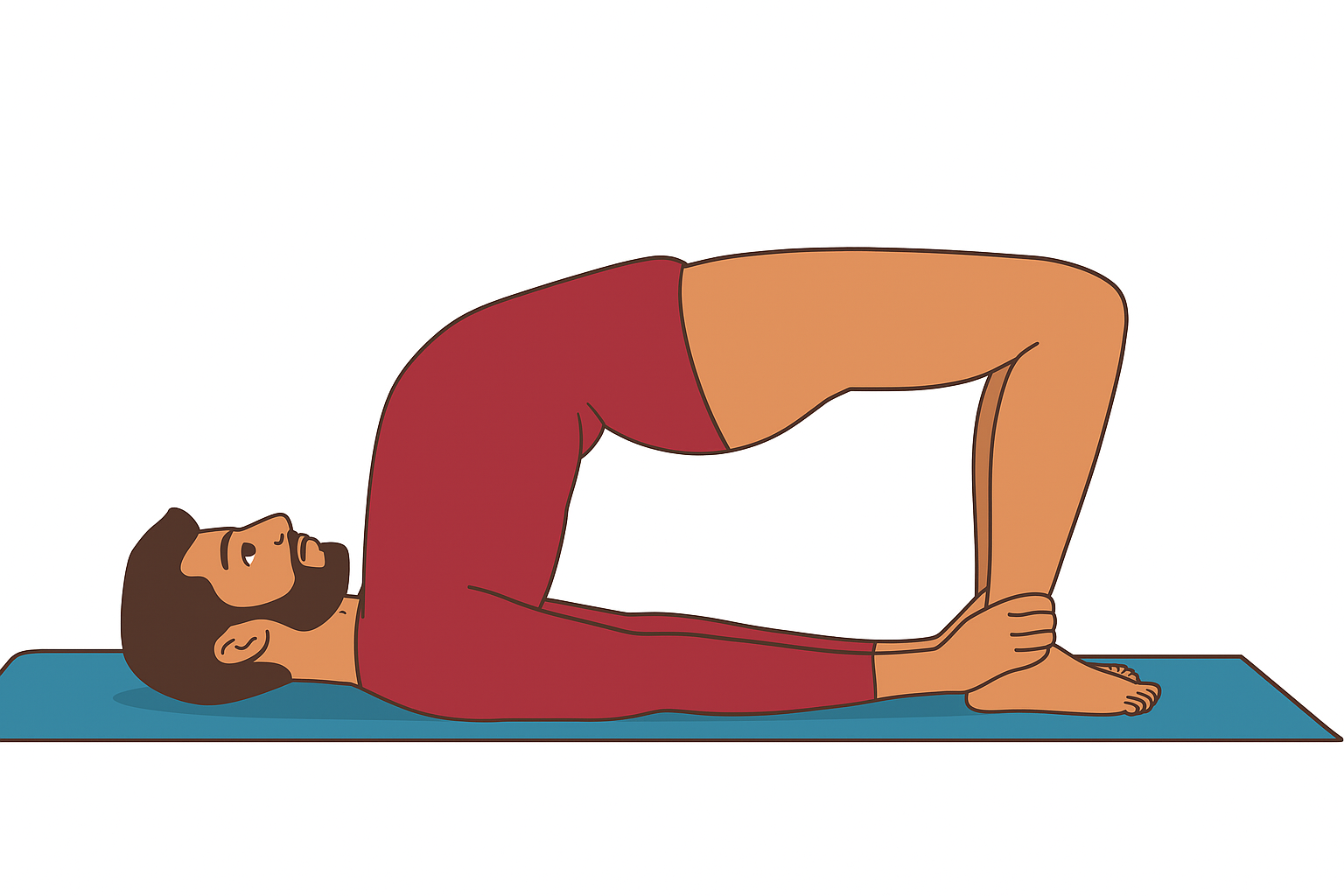
Setubandhasana (Bridge Pose) – Steps, Benefits and Precautions
Yoga has been an important part of Indian culture for thousands of years. It is not only a physical exercise but also a way to balance the body and mind. Among the many yoga postures, Setubandhasana holds a special place. The word “Setu” means bridge and “Bandha” means lock or bind. When a person performs this asana, the body looks like a bridge, hence the name Bridge Pose.
This posture is simple to learn and can be practiced by most people, except those with certain medical conditions. It is especially useful for students, office workers, and anyone who spends long hours sitting, as it helps relieve back strain and improves posture.
Table of Contents
How to Practice Setubandhasana
The practice of Setubandhasana should be done on a yoga mat or a flat surface. It is best performed in the morning on an empty stomach, or at least 3–4 hours after a meal.
Steps for Practice
- Starting Position – Lie flat on your back in Shavasana (relaxation pose) with arms by your side and legs straight.
- Bend the Knees – Slowly bend both your legs at the knees and bring the heels close to the buttocks. Keep the feet flat on the floor.
- Hold the Ankles – Place both arms alongside the body. Hold your ankles with your hands. Ensure that your knees and feet are in one straight line. The gap between the feet should be the same as the distance between your shoulders.
- Inhale and Lift – While breathing in, gently raise your buttocks, hips, and trunk upward. Keep lifting until your chest touches your chin or as much as you comfortably can. The body should form a bridge-like shape.
- Maintain the Pose – Remain in this position for 10–30 seconds. Breathe normally and keep your focus on the stretch in your chest, back, and abdomen.
- Return to Starting Position – While exhaling, slowly lower your trunk and buttocks back to the ground. Relax your body in Shavasana.
Dos and Don’ts of Setubandhasana
Like all yoga postures, Setubandhasana must be performed correctly. Wrong technique can cause discomfort or injury. Here are some important points to remember:
Dos:
- Keep the feet close to the buttocks.
- Ensure the knees are vertical to the ground, not leaning outward.
- Raise the body smoothly without jerks.
- Breathe steadily and stay calm while holding the posture.
Don’ts:
- Do not perform this asana if you are suffering from Cervical Spondylitis or severe neck problems.
- Avoid lifting the body with sudden force or pressure.
- Do not practice immediately after eating.
- People with back injury should practice only under expert guidance.
Benefits of Setubandhasana
Setubandhasana is a wonderful yoga posture that provides many physical and mental benefits. Some of the key advantages are:
- Relieves Back Strain – This pose reduces stress on the lower back and spine, making it useful for people with mild back pain due to long sitting hours.
- Strengthens Back Muscles – Regular practice tones and strengthens the spinal muscles, hips, and thighs.
- Improves Flexibility – It increases flexibility in the spine and makes the body more active and energetic.
- Stretches Abdominal Organs – The posture gently massages the abdominal organs like the colon, improving digestion and metabolism.
- Enhances Lung Capacity – By expanding the chest, it helps the lungs to take in more oxygen. This is very useful for students and athletes who need strong breathing capacity.
- Calms the Mind – The posture improves blood circulation and helps release stress, making the practitioner feel peaceful and relaxed.
- Boosts Posture and Confidence – With stronger muscles and better breathing, the body feels lighter and the mind becomes more confident.
Precautions
Even though Setubandhasana is simple, it must be practiced carefully:
- People with neck pain, cervical spondylitis, or recent surgery should avoid it.
- Pregnant women should practice only under expert supervision.
- Beginners should not stay in the posture for too long. Start with 10 seconds and increase gradually.
- Always come down slowly while releasing the pose to prevent injury.
Conclusion
Setubandhasana or Bridge Pose is an easy yet powerful yoga asana that benefits the body and mind. It strengthens the back, improves lung capacity, and keeps the spine flexible. For students, it is particularly helpful as it reduces stress, improves concentration, and keeps the body active.
Regular practice of this posture, combined with proper breathing, can improve overall health and well-being. However, one must remember to follow the correct steps, respect the dos and don’ts, and avoid the pose if there are medical restrictions.
In today’s busy lifestyle, where back pain, poor posture, and stress have become common problems, Setubandhasana offers a natural and effective solution. Just a few minutes of practice every day can help you feel lighter, stronger, and more positive.
Subscribe to us on YouTube and try our quizzes on this website to keep your exam preparation on track.