Have you ever wondered what your body is made of? The answer is — cells! Every living thing, from a tiny plant to a human, is made up of cells. They are so small that you need a microscope to see them — but they do very big jobs
What is a Cell?
A cell is the smallest unit of life. It is like a small room that keeps our body alive and working.
- All living things are made of cells.
- Cells are known as the building blocks of life.
- Cell theory (1839): Given by Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden.
- Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1665.
- Robert Brown discovered the nucleus in 1831.
- The study of cells is called Cytology.

Types of Living Organisms
- Unicellular organisms: Made of just one cell (e.g. bacteria, yeast).
- Multicellular organisms: Made of many cells (e.g. plants, animals, humans).
Levels of Body Structure
Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ System → Whole Organism
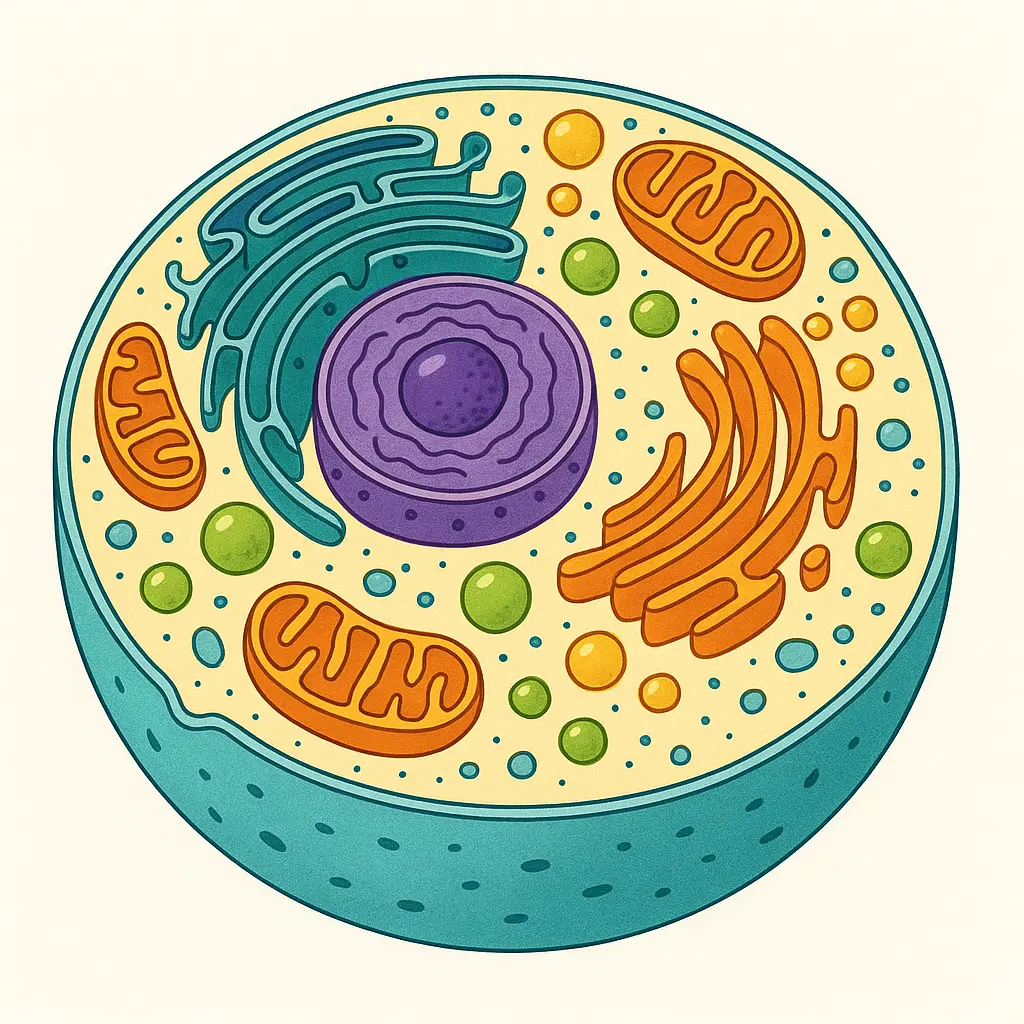
Cell Structure: Basic Components of the Cell
Here are the key parts of a cell and what they do:
| Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | Covers the cell; controls what goes in or out. |
| Protoplasm | Jelly-like substance inside the cell. |
| Cytoplasm | Fluid between the nucleus and cell membrane. |
| Mitochondria | Makes energy for the cell. |
| Golgi Bodies | Pack and send proteins and fats. |
| Lysosome | Destroys waste and damaged parts. |
| Ribosome | Makes proteins. |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Makes and transports proteins and fats. |
| Vacuoles | Store water, food, and waste. |
| Centrosome | Helps the cell divide (only in animal cells). |
| Nucleus | Controls the cell and stores DNA. |
| Plastids | Found in plants; used for food and color. |
| Cilia and Flagella | Help in cell movement. |

Cell Membrane
- It covers the cell like a skin.
- It allows useful things (like oxygen and food) to enter.
- It blocks harmful things from coming in or going out.
Protoplasm
- It is the jelly-like substance inside the cell.
- It has water, proteins, fats, minerals, and enzymes.
Cytoplasm
All cell activities happen here.
It is the fluid part of the protoplasm between the nucleus and cell membrane.
Mitochondria: The Powerhouse
- Discovered by Richard Altman in 1890.
- Called the “powerhouse” of the cell.
- Produces energy in the form of ATP.
- Helps in respiration and breaking down fats and proteins.
Golgi Bodies
- Discovered by Camillo Golgi (1897).
- Modify and send proteins/fats to different parts of the cell.
- Help in making carbohydrates.
Lysosome: The Cell Cleaner
- Found by Christian de Duve.
- Destroys old and damaged parts of the cell.
- Called the “suicide bag” of the cell.
- Not found in Red Blood Cells (RBCs). Damaged RBCs go to the spleen (RBC graveyard).
Ribosome: Protein Maker
- Discovered by George Emil Palade (1950).
- Makes proteins using information from mRNA.
- Uses tRNA to collect building blocks (amino acids).
- Known as the “protein factory”.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Connected to the nucleus.
- Has two types:
- Rough ER – with ribosomes, makes proteins.
- Smooth ER – no ribosomes, makes fats.
Vacuole: The Storage Tank
- Stores water, nutrients, and waste.
- Helps keep the shape and pressure of the cell.
- Larger in plant cells than in animal cells.
Centrosome: Cell Division Helper
- Found only in animal cells.
- Helps in cell division.
- Not found in brain cells (that’s why nerve cells don’t divide).
Nucleus: The Brain of the Cell
- Controls all cell functions.
- Has a web-like structure called chromatin.
- Chromatin becomes chromosomes during cell division.
- Human cells have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs).
- Chromosomes contain DNA and RNA, which pass traits from parents to children.
Nucleolus
- Found inside the nucleus.
- Helps make ribosomes.
Cilia and Flagella
- Flagella: Long tails that help a cell move.
- Cilia: Short hairs that move things across the cell surface.
Plastids (Only in Plants)
| Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Chloroplast | Makes food using sunlight (green in color) |
| Chromoplast | Gives color to parts like flowers or fruits |
| Leucoplast | Stores food in roots, seeds, etc. |
Types of Cells
| Eukaryotic Cell | Prokaryotic Cell |
|---|---|
| Has a nucleus | No nucleus |
| Large and complex | Small and simple |
| Found in animals and plants | Found in bacteria and mycoplasma |

Fun Cell Facts!
- Smallest human cell: Sperm
- Largest human cell: Ovum (egg cell)
- Longest cell: Sciatic nerve
- Smallest cell in the world: Mycoplasma
- Largest cell in the world: Ostrich egg
Conclusion
Cells are the tiny but powerful units of life. They do everything from giving you energy to helping you grow. Even though you can’t see them, your body wouldn’t work without them!
Cells may be small — but they’re truly superheroes of life.
Watch Full video on youtube