Skip to contentKabaddi: History, Rules and Measurements
Origin and Evolution:
- Origin: Kabaddi originated in Tamil Nadu, India.
- Early Regulations: The initial rules for Kabaddi were established in the early 20th century by Deccan Gymkhana.
- Historical Milestones:
- 1923: Hind Vijay Gymkhana, Baroda, formalized the rules and organized the first All India competition.
- 1934: The All Maharashtra Physical Council revised the rules.
- 1987: The first international competition was held in Calcutta during the SAF Games.
- 2004: The International Kabaddi Federation (IKF) was founded in Mumbai.
Major Organizations:
- Asian Amateur Kabaddi Federation (AAKF): Established in 1978, headquartered in Jaipur, Rajasthan.
- Amateur Kabaddi Federation of India (AKFI): Formed in 1973, based in Calcutta.
- Kabaddi Federation of India: Established in 1950.
Olympics and Asian Games:
- Kabaddi has not yet been included in the Olympic Games.
- Included in the Asian Games since 1990 in Beijing for men, and since 2010 in Guangzhou for women.
Awards:
- First Arjuna Award: 1972, Sadanand Shetty.
- First Dronacharya Award: 2002, E. Prasad Rao.
Name of Kabaddi in Different Region:
- Hu-Tu-Tu: Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat.
- Chu-do-do: Tamil Nadu, Mysore.
- He-du-du: Kerala, Bengal.
- Chedugudu: Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka.
- Hu-Du-Du: Bangladesh.
- Gu-Du: Sri Lanka.
- CHUB: Indonesia.
- Kabaddi: Pakistan.
- Bhavatik: Maldives.
- Do-Do: Nepal.
Styles of Kabaddi:
- Sanjeevani Kabaddi:
- Each team has 7 players.
- Players revive one teammate when an opponent is put out.
- Matches last 40 minutes with a 5-minute halftime break.
- Gaminee Kabaddi:
- Each team has 7 players.
- Out players remain out until all teammates are out.
- No time limit; game continues until one team scores 5 or 7 points.
- Amar Kabaddi:
- No time limit.
- Players remain in play after being tagged; each tag scores a point.
- Circle Kabaddi (Punjabi Kabaddi):
- Played in a circular field with a 22-meter diameter.
- Includes variations like Lambi Kabaddi, Saunchi Kabaddi, and Goongi Kabaddi.
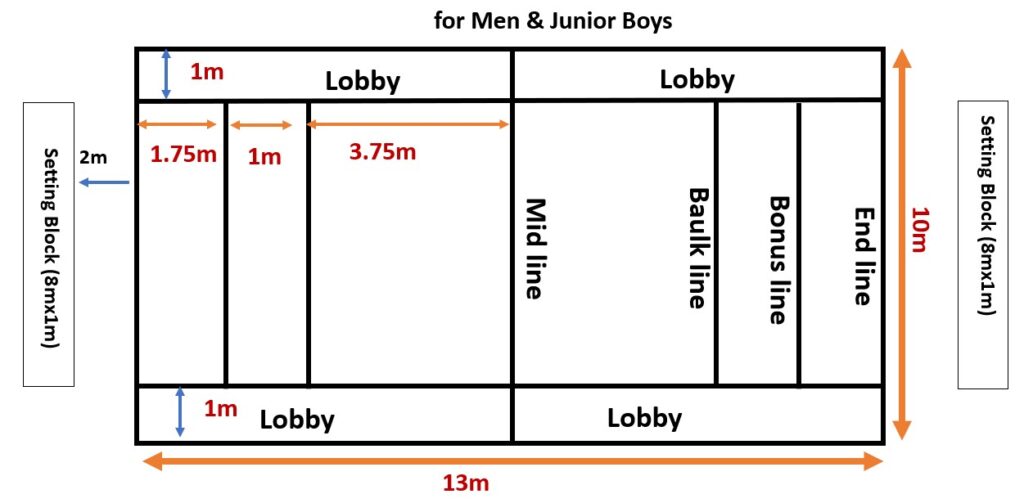
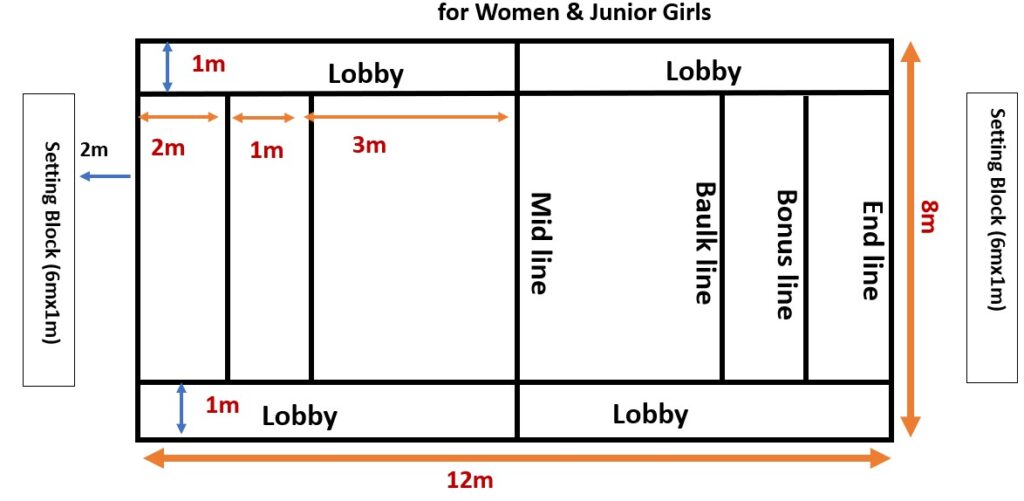
Court Measurements:
- Men and Junior Boys: 13m x 10m with specific markings for the baulk line, bonus line, and lobby.

- Women and Junior Girls: 12m x 8m with similar markings adjusted for size.

Rules of Kabaddi:
Player Regulations:
- Teams consist of 12 players (7 on the field, 5 substitutes).
- Players must have clipped nails and wear no ornaments.
- Oil or soft substances are prohibited.
- Shoes are mandatory on mat surfaces.
- Distinct numbers are required on jerseys (4 inches in front, 6 inches at the back).
Substitution Rules:
- Five reserved players can be substituted, except for suspended players.
- Substitutions occur during timeouts or intervals.
Timeouts:
- Each team is allowed two 30-second timeouts per half.
- Official timeouts can be called by the referee for injuries or interruptions.
Match Start and Conduct:
- Toss: Determines the first raid.
- Out of Bounds: Players are out if any body part touches outside the boundary unless contact with the playfield is maintained.
- Raid Time: Each raid has a 30-second limit.
- Chant: Raiders must continuously chant “KABADDI” during the raid.
Scoring:
- LONA: Scored when all opponents are out, earning two extra points.
- Bonus Point: Awarded when a raider crosses the bonus line with at least 6 players on the field.
Tie-Breaking:
- Teams alternate 5 raids each; if still tied, a golden raid decides the winner.
Penalties:
- Green Card: Warning.
- Yellow Card: 2-minute suspension.
- Red Card: Ejection from the match or tournament.
Officials in Kabaddi
1. Referee:
- Authority: The primary official who has the final authority over the game.
- Duties:
- Starts and stops the match.
- Enforces rules and regulations.
- Issues warnings and cards (green, yellow, red) to players.
- Resolves disputes and makes decisions on any points of contention.
- Ensures the game is played in a fair manner.
2. Umpires:
- Number: Two umpires assist the referee.
- Duties:
- Monitor player conduct and enforce rules.
- Assist the referee in making decisions.
- Observe the play from different angles to ensure all rules are followed.
- Can also issue warnings and signal fouls.
3. Scorer:
- Duties:
- Maintains the official score of the match.
- Records points scored by each team.
- Keeps track of players who are out and those who revive.
- Documents timeouts, substitutions, and any disciplinary actions taken during the match.
4. Assistant Scorers:
- Number: Two assistant scorers.
- Duties:
- Assist the main scorer in keeping accurate records.
- Handle specific tasks such as timing raids and monitoring the 30-second raid rule.
- Ensure that player and team statistics are accurately recorded.
You Might Also Like